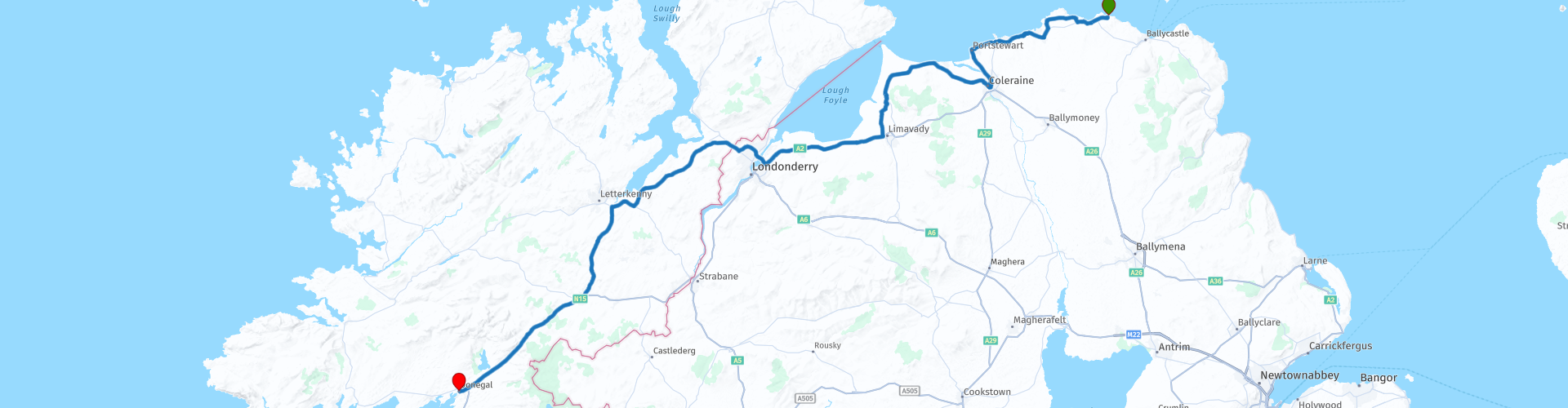
Ballintoy to Donegal

This route was brought to you by:
RouteXpert Wil van der Helm
Last edit: 04-02-2019
 Route Summary
Route Summary  Share this route
Share this route 




Animation

Verdict


Duration
2h 49m

Mode of travel
Car or motorcycle

Distance
171.26 km

Countries



Dunluce Castle
 RouteXpert Review
RouteXpert Review This route is described in more detail in the northern part of Northern Ireland. The roads are fine, asphalted in hilly terrain with beautiful white beaches. The most eye-catching sights have been named and detailed information can be found on the www.
Giant's Causeway (RP2)
This is a vast walking area with characteristic coastline of mythical proportions. Extensive info including Wild Atlantic Way
Bushmills (RP3)
In Bushmills, the famous Irish whiskey distillery of the same name has been established since 1608 and can be visited.
Dunluce Castle (RP4)
At this ruin is a parking lot with cafe.
Mussenden Temple (RP8)
Is part of the Park National Trust - Downhill Demesne what to visit. For a photo opportunity; at RP8 you can drive up the beach and you have a beautiful view of Mussenden Temple.
If you want to visit the Inoshowen peninsula with Mailn Head (lighthouse at a rugged cape with swirling sea) then there are 2 options, or you take the ferry at Magillan (RP9), or you make the detour of RP10. Do count on an extra 100km. Do not forget the piece R238 between Buncrana and Fahan (or vice versa).
The sequel is via Letterkenny the fastest way to Donegal (city) and ends at the square in the center.
If you are staying in Donegal and you love Irish Traditionals, be sure to visit The Reel Inn where live folkloristic music is played every night.

Mussenden Temple

Giant's Causeway
 Usage
Usage Want to download this route?
You can download the route for free without MyRoute-app account. To do so, open the route and click 'save as'. Want to edit this route?
No problem, start by opening the route. Follow the tutorial and create your personal MyRoute-app account. After registration, your trial starts automatically.  Disclaimer
Disclaimer
Use of this GPS route is at your own expense and risk. The route has been carefully composed and checked by a MyRoute-app accredited RouteXpert for use on TomTom, Garmin and MyRoute-app Navigation.
Changes may nevertheless have occurred due to changed circumstances, road diversions or seasonal closures. We therefore recommend checking each route before use.
Preferably use the route track in your navigation system. More information about the use of MyRoute-app can be found on the website under 'Community' or 'Academy'.
Changes may nevertheless have occurred due to changed circumstances, road diversions or seasonal closures. We therefore recommend checking each route before use.
Preferably use the route track in your navigation system. More information about the use of MyRoute-app can be found on the website under 'Community' or 'Academy'.

Ulster
About this region
Ulster (; Irish: Ulaidh [ˈʊlˠiː, ˈʊlˠə] or Cúige Uladh [ˌkuːɟə ˈʊlˠə, - ˈʊlˠuː]; Ulster Scots: Ulstèr or Ulster) is one of the four traditional Irish provinces, in the north of Ireland. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); the remaining three are in the Republic of Ireland.
It is the second-largest (after Munster) and second-most populous (after Leinster) of Ireland's four provinces, with Belfast being its biggest city. Unlike the other provinces, Ulster has a high percentage of Protestants, making up almost half of its population. English is the main language and Ulster English the main dialect. A minority also speak Irish, and there are Gaeltachtaí (Irish-speaking regions) in southern County Londonderry, the Gaeltacht Quarter, Belfast, and in County Donegal; collectively, these three regions are home to a quarter of the total Gaeltacht population of Ireland. Ulster-Scots is also spoken. Lough Neagh, in the east, is the largest lake in the British Isles, while Lough Erne in the west is one of its largest lake networks. The main mountain ranges are the Mournes, Sperrins, Croaghgorms and Derryveagh Mountains.
Historically, Ulster lay at the heart of the Gaelic world made up of Gaelic Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man. According to tradition, in ancient Ireland it was one of the fifths (Irish: cúige) ruled by a rí ruirech, or "king of over-kings". It is named after the overkingdom of Ulaid, in the east of the province, which was in turn named after the Ulaid folk. The other overkingdoms in Ulster were Airgíalla and Ailech. After the Norman invasion of Ireland in the 12th century, eastern Ulster was conquered by the Anglo-Normans and became the Earldom of Ulster. By the late 14th century the Earldom had collapsed and the O'Neill dynasty had come to dominate most of Ulster, claiming the title King of Ulster. Ulster became the most thoroughly Gaelic and independent of Ireland's provinces. Its rulers resisted English encroachment but were defeated in the Nine Years' War (1594–1603). King James I then colonised Ulster with English-speaking Protestant settlers from Great Britain, in the Plantation of Ulster. This led to the founding of many of Ulster's towns. The inflow of Protestant settlers and migrants also led to bouts of sectarian violence with Catholics, notably during the 1641 rebellion and the Armagh disturbances. Along with the rest of Ireland, Ulster became part of the United Kingdom in 1801. In the early 20th century, moves towards Irish self-rule were opposed by many Ulster Protestants, sparking the Home Rule Crisis. This, and the subsequent Irish War of Independence, led to the partition of Ireland. Six Ulster counties became Northern Ireland, a self-governing territory within the United Kingdom, while the rest of Ireland became the Irish Free State, now the Republic of Ireland.
The term Ulster has no official function for local government purposes in either country. However, for the purposes of ISO 3166-2, Ulster is used to refer to the three counties of Cavan, Donegal and Monaghan only, which are given country sub-division code "IE-U". The name is also used by various organisations such as cultural and sporting bodies.
Read more on Wikipedia
It is the second-largest (after Munster) and second-most populous (after Leinster) of Ireland's four provinces, with Belfast being its biggest city. Unlike the other provinces, Ulster has a high percentage of Protestants, making up almost half of its population. English is the main language and Ulster English the main dialect. A minority also speak Irish, and there are Gaeltachtaí (Irish-speaking regions) in southern County Londonderry, the Gaeltacht Quarter, Belfast, and in County Donegal; collectively, these three regions are home to a quarter of the total Gaeltacht population of Ireland. Ulster-Scots is also spoken. Lough Neagh, in the east, is the largest lake in the British Isles, while Lough Erne in the west is one of its largest lake networks. The main mountain ranges are the Mournes, Sperrins, Croaghgorms and Derryveagh Mountains.
Historically, Ulster lay at the heart of the Gaelic world made up of Gaelic Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man. According to tradition, in ancient Ireland it was one of the fifths (Irish: cúige) ruled by a rí ruirech, or "king of over-kings". It is named after the overkingdom of Ulaid, in the east of the province, which was in turn named after the Ulaid folk. The other overkingdoms in Ulster were Airgíalla and Ailech. After the Norman invasion of Ireland in the 12th century, eastern Ulster was conquered by the Anglo-Normans and became the Earldom of Ulster. By the late 14th century the Earldom had collapsed and the O'Neill dynasty had come to dominate most of Ulster, claiming the title King of Ulster. Ulster became the most thoroughly Gaelic and independent of Ireland's provinces. Its rulers resisted English encroachment but were defeated in the Nine Years' War (1594–1603). King James I then colonised Ulster with English-speaking Protestant settlers from Great Britain, in the Plantation of Ulster. This led to the founding of many of Ulster's towns. The inflow of Protestant settlers and migrants also led to bouts of sectarian violence with Catholics, notably during the 1641 rebellion and the Armagh disturbances. Along with the rest of Ireland, Ulster became part of the United Kingdom in 1801. In the early 20th century, moves towards Irish self-rule were opposed by many Ulster Protestants, sparking the Home Rule Crisis. This, and the subsequent Irish War of Independence, led to the partition of Ireland. Six Ulster counties became Northern Ireland, a self-governing territory within the United Kingdom, while the rest of Ireland became the Irish Free State, now the Republic of Ireland.
The term Ulster has no official function for local government purposes in either country. However, for the purposes of ISO 3166-2, Ulster is used to refer to the three counties of Cavan, Donegal and Monaghan only, which are given country sub-division code "IE-U". The name is also used by various organisations such as cultural and sporting bodies.
View region
 Statistics
Statistics  9
9Amount of RX reviews (Ulster)
 14603
14603Amount of visitors (Ulster)
 1080
1080Amount of downloads (Ulster)
 Route Collections in this region
Route Collections in this region Complete tour of Ireland
Ireland is a beautiful country to drive. This collection contains 10 connecting routes that take you past the most beautiful, cities, villages, sights and wonders of nature.
All routes include reviews, route points for hotels, restaurants and POI.
The Irish population is very friendly and hospitable, in every village there are several pubs and restaurants where you can enjoy Irish cuisine.
There are several (historical) sights included in the routes, here is a summary overview per route, in the reviews of the routes you will find more details.
IRL1; Belvedere House & Garden Parks, Charleville Castle and the Ruins of Clonmacnoise
IRL2; Sky Road, Connemara Natural Park and Kylemoore Abbey.
IRL3; The Burren, the peninsulas Lettermore, Tiermee and Teach Mor, Blackhead and the Cliffs of Moher.
IRL4; Bunratty Castle, Folk Park and King Johns Castle.
IRL5; Ring of Kerry and Skellig Ring, this is without a doubt the most beautiful part of the Ring of Kerry. With a beautiful view of Little Skellig and Skellig Michael, the islands where the latest Star Wars film was shot.
IRL6; Ring of Beare, Glenngariff Woods Nature Reserve and one of the most beautiful panoramas in Ireland: "Ladies View".
IRL7; Killarney National Park with Molls Gap, Ladies View, the Healy Pass and Priest's Leap (very narrow winding route with partly very bad road surface) and Mizen Head.
IRL8; Blarney Castle, Cahir Castle, Killkenny Castle and Saint Canice's Cathedral.
IRL9; Dunmore Caves, SS Dunbrody Irish Emigrants ship, the ruins of Dunbrody Abbey and Garden and Kilkenny Castle.
IRL10; the ruins of the Black Castle, The Altamont Gardens, Powerscourt Gardens and Waterfall and St. Patricks Cathedral.
The routes are mainly country roads, often with beautiful curves, but sometimes very narrow or of poor quality. Driving experience is required, partly because of driving on the left side of the road.
You drive through nature parks and pass such as the Healy Pass, Conner Pass, Priest's Leap and Molls Gap. Two beautiful routes are the famous Ring of Kerry (IRL5) and Ring of Beare (IRL6). These are long journeys with many beautiful things along the way, so staying overnight while on the road is highly recommended. It can also be very busy on these routes in the weekends.
The other two routes in this collection is The Wild Atlantic Way from North-South and from South to North. This route is a sensational journey past towering cliffs and lively villages and towns, past hidden beaches and beautiful bays. This route follows the West Coast and you do multiple places from the other routes. The review of the route contains more details and for even more information I refer to https://www.wildatlanticway.com/home
All routes in this collection are all beautiful and challenging and can be driven by car or motorcycle.
Have fun with these routes.
All routes include reviews, route points for hotels, restaurants and POI.
The Irish population is very friendly and hospitable, in every village there are several pubs and restaurants where you can enjoy Irish cuisine.
There are several (historical) sights included in the routes, here is a summary overview per route, in the reviews of the routes you will find more details.
IRL1; Belvedere House & Garden Parks, Charleville Castle and the Ruins of Clonmacnoise
IRL2; Sky Road, Connemara Natural Park and Kylemoore Abbey.
IRL3; The Burren, the peninsulas Lettermore, Tiermee and Teach Mor, Blackhead and the Cliffs of Moher.
IRL4; Bunratty Castle, Folk Park and King Johns Castle.
IRL5; Ring of Kerry and Skellig Ring, this is without a doubt the most beautiful part of the Ring of Kerry. With a beautiful view of Little Skellig and Skellig Michael, the islands where the latest Star Wars film was shot.
IRL6; Ring of Beare, Glenngariff Woods Nature Reserve and one of the most beautiful panoramas in Ireland: "Ladies View".
IRL7; Killarney National Park with Molls Gap, Ladies View, the Healy Pass and Priest's Leap (very narrow winding route with partly very bad road surface) and Mizen Head.
IRL8; Blarney Castle, Cahir Castle, Killkenny Castle and Saint Canice's Cathedral.
IRL9; Dunmore Caves, SS Dunbrody Irish Emigrants ship, the ruins of Dunbrody Abbey and Garden and Kilkenny Castle.
IRL10; the ruins of the Black Castle, The Altamont Gardens, Powerscourt Gardens and Waterfall and St. Patricks Cathedral.
The routes are mainly country roads, often with beautiful curves, but sometimes very narrow or of poor quality. Driving experience is required, partly because of driving on the left side of the road.
You drive through nature parks and pass such as the Healy Pass, Conner Pass, Priest's Leap and Molls Gap. Two beautiful routes are the famous Ring of Kerry (IRL5) and Ring of Beare (IRL6). These are long journeys with many beautiful things along the way, so staying overnight while on the road is highly recommended. It can also be very busy on these routes in the weekends.
The other two routes in this collection is The Wild Atlantic Way from North-South and from South to North. This route is a sensational journey past towering cliffs and lively villages and towns, past hidden beaches and beautiful bays. This route follows the West Coast and you do multiple places from the other routes. The review of the route contains more details and for even more information I refer to https://www.wildatlanticway.com/home
All routes in this collection are all beautiful and challenging and can be driven by car or motorcycle.
Have fun with these routes.
View Route Collection
12 Routes
6892.56 km
145h 19m
