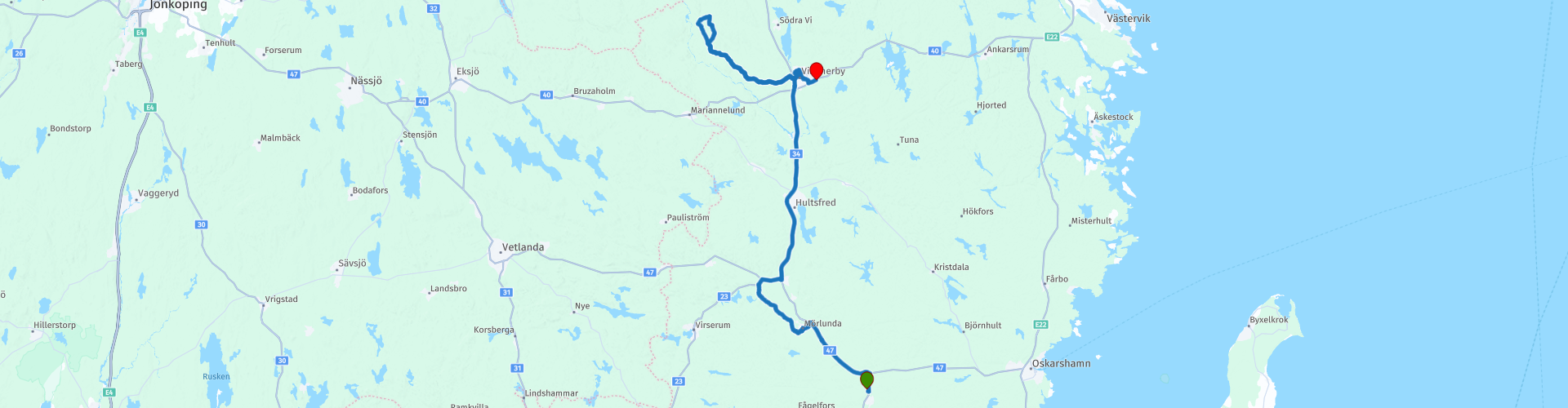
Berga Vimmerby

This route was brought to you by:
RouteXpert Evert Kuiken
Last edit: 22-12-2020
 Route Summary
Route Summary  Share this route
Share this route 




Animation

Verdict


Duration
2h 20m

Mode of travel
Car or motorcycle

Distance
122.17 km

Countries


De weg bij de Kvilleken
 RouteXpert Review
RouteXpert Review We drive past Vimmerby to the Norra Kvill nature park (RP5) and visit the oldest (1000 years!) Thick oak Kvilliken or Rumskulla oak (RP6). Here you can walk great. Then put the engine down at RP5. There is the entrance to the nature park. The oak is a little further on the route back to Vimmerby. You can easily walk there in a few minutes.
We drive back to Vimmerby where Astrid Lindgren was born. You can go to the museum in her birth house (Astrid Lindgren Näs, RP9) or to the amusement park, watch Pippi, Karlson from the roof etc. (RP8). You can eat in the park or in the city, for example at Mamas pizzeria or at the Chinese Big Wond (Sweet Chili). There are no real good restaurants in Vimmerby. You can also grab a bite to eat at the campsite on the terrace by the water. You can also spend the night there at the campsite (RP11).
We skipped the amusement park: not our thing. And we picked up the next day's route. We ignored the Vimmerby Camping Nossenbaden (RP11) campsite. If you want that too, start the next day's route towards Västervik and Vättern in Vimmerby, otherwise you will drive back and forth through the campsite.
The route gets 5 stars from me. The roads are fine and varied: a few stretches of gravel, a few stretches on larger roads. The sights are excellent. The landscape is very beautiful with a lot of forest.

Kvilleken

Västervik
 Links
Links  Usage
Usage Want to download this route?
You can download the route for free without MyRoute-app account. To do so, open the route and click 'save as'. Want to edit this route?
No problem, start by opening the route. Follow the tutorial and create your personal MyRoute-app account. After registration, your trial starts automatically.  Disclaimer
Disclaimer
Use of this GPS route is at your own expense and risk. The route has been carefully composed and checked by a MyRoute-app accredited RouteXpert for use on TomTom, Garmin and MyRoute-app Navigation.
Changes may nevertheless have occurred due to changed circumstances, road diversions or seasonal closures. We therefore recommend checking each route before use.
Preferably use the route track in your navigation system. More information about the use of MyRoute-app can be found on the website under 'Community' or 'Academy'.
Changes may nevertheless have occurred due to changed circumstances, road diversions or seasonal closures. We therefore recommend checking each route before use.
Preferably use the route track in your navigation system. More information about the use of MyRoute-app can be found on the website under 'Community' or 'Academy'.

Kalmar ln
About this region
Copenhagen (Danish: København [kʰøpm̩ˈhɑwˀn] (listen)) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark. As of 1 January 2021, the city had a population of 799,033 (638,117 in Copenhagen Municipality, 103,677 in Frederiksberg Municipality, 42,670 in Tårnby Municipality, and 14,569 in Dragør Municipality). It forms the core of the wider urban area of Copenhagen (population 1,336,982) and the Copenhagen metropolitan area (population 2,057,142). Copenhagen is situated on the eastern coast of the island of Zealand; another portion of the city is located on Amager, and it is separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the strait of Øresund. The Øresund Bridge connects the two cities by rail and road.
Originally a Viking fishing village established in the 10th century in the vicinity of what is now Gammel Strand, Copenhagen became the capital of Denmark in the early 15th century. Beginning in the 17th century, it consolidated its position as a regional centre of power with its institutions, defences, and armed forces. During the Renaissance the city served as the de facto capital being the seat of the monarchy of the Kalmar Union, governing the entire present day Nordic region in a personal union with Sweden and Norway ruled by the Danish monarch serving as the head of state. The city flourished as the cultural and economic center of Scandinavia under the union for well over 120 years, starting in the 15th century up until the beginning of the 16th century when the union was dissolved with Sweden leaving the union through a rebellion. After a plague outbreak and fire in the 18th century, the city underwent a period of redevelopment. This included construction of the prestigious district of Frederiksstaden and founding of such cultural institutions as the Royal Theatre and the Royal Academy of Fine Arts. After further disasters in the early 19th century when Horatio Nelson attacked the Dano-Norwegian fleet and bombarded the city, rebuilding during the Danish Golden Age brought a Neoclassical look to Copenhagen's architecture. Later, following the Second World War, the Finger Plan fostered the development of housing and businesses along the five urban railway routes stretching out from the city centre.
Since the turn of the 21st century, Copenhagen has seen strong urban and cultural development, facilitated by investment in its institutions and infrastructure. The city is the cultural, economic and governmental centre of Denmark; it is one of the major financial centres of Northern Europe with the Copenhagen Stock Exchange. Copenhagen's economy has seen rapid developments in the service sector, especially through initiatives in information technology, pharmaceuticals and clean technology. Since the completion of the Øresund Bridge, Copenhagen has become increasingly integrated with the Swedish province of Scania and its largest city, Malmö, forming the Øresund Region. With a number of bridges connecting the various districts, the cityscape is characterised by parks, promenades, and waterfronts. Copenhagen's landmarks such as Tivoli Gardens, The Little Mermaid statue, the Amalienborg and Christiansborg palaces, Rosenborg Castle, Frederik's Church, Børsen and many museums, restaurants and nightclubs are significant tourist attractions.
Copenhagen is home to the University of Copenhagen, the Technical University of Denmark, Copenhagen Business School and the IT University of Copenhagen. The University of Copenhagen, founded in 1479, is the oldest university in Denmark. Copenhagen is home to the F.C. Copenhagen. The annual Copenhagen Marathon was established in 1980. Copenhagen is one of the most bicycle-friendly cities in the world.
Movia is the public mass transit company serving all of eastern Denmark, except Bornholm. The Copenhagen Metro, launched in 2002, serves central Copenhagen. Additionally, the Copenhagen S-train, the Lokaltog (private railway), and the Coast Line network serve and connect central Copenhagen to outlying boroughs. Serving roughly 2.5 million passengers a month, Copenhagen Airport, Kastrup, is the busiest airport in the Nordic countries.
Read more on Wikipedia
Originally a Viking fishing village established in the 10th century in the vicinity of what is now Gammel Strand, Copenhagen became the capital of Denmark in the early 15th century. Beginning in the 17th century, it consolidated its position as a regional centre of power with its institutions, defences, and armed forces. During the Renaissance the city served as the de facto capital being the seat of the monarchy of the Kalmar Union, governing the entire present day Nordic region in a personal union with Sweden and Norway ruled by the Danish monarch serving as the head of state. The city flourished as the cultural and economic center of Scandinavia under the union for well over 120 years, starting in the 15th century up until the beginning of the 16th century when the union was dissolved with Sweden leaving the union through a rebellion. After a plague outbreak and fire in the 18th century, the city underwent a period of redevelopment. This included construction of the prestigious district of Frederiksstaden and founding of such cultural institutions as the Royal Theatre and the Royal Academy of Fine Arts. After further disasters in the early 19th century when Horatio Nelson attacked the Dano-Norwegian fleet and bombarded the city, rebuilding during the Danish Golden Age brought a Neoclassical look to Copenhagen's architecture. Later, following the Second World War, the Finger Plan fostered the development of housing and businesses along the five urban railway routes stretching out from the city centre.
Since the turn of the 21st century, Copenhagen has seen strong urban and cultural development, facilitated by investment in its institutions and infrastructure. The city is the cultural, economic and governmental centre of Denmark; it is one of the major financial centres of Northern Europe with the Copenhagen Stock Exchange. Copenhagen's economy has seen rapid developments in the service sector, especially through initiatives in information technology, pharmaceuticals and clean technology. Since the completion of the Øresund Bridge, Copenhagen has become increasingly integrated with the Swedish province of Scania and its largest city, Malmö, forming the Øresund Region. With a number of bridges connecting the various districts, the cityscape is characterised by parks, promenades, and waterfronts. Copenhagen's landmarks such as Tivoli Gardens, The Little Mermaid statue, the Amalienborg and Christiansborg palaces, Rosenborg Castle, Frederik's Church, Børsen and many museums, restaurants and nightclubs are significant tourist attractions.
Copenhagen is home to the University of Copenhagen, the Technical University of Denmark, Copenhagen Business School and the IT University of Copenhagen. The University of Copenhagen, founded in 1479, is the oldest university in Denmark. Copenhagen is home to the F.C. Copenhagen. The annual Copenhagen Marathon was established in 1980. Copenhagen is one of the most bicycle-friendly cities in the world.
Movia is the public mass transit company serving all of eastern Denmark, except Bornholm. The Copenhagen Metro, launched in 2002, serves central Copenhagen. Additionally, the Copenhagen S-train, the Lokaltog (private railway), and the Coast Line network serve and connect central Copenhagen to outlying boroughs. Serving roughly 2.5 million passengers a month, Copenhagen Airport, Kastrup, is the busiest airport in the Nordic countries.
View region
 Statistics
Statistics  4
4Amount of RX reviews (Kalmar ln)
 8274
8274Amount of visitors (Kalmar ln)
 252
252Amount of downloads (Kalmar ln)
 Route Collections in this region
Route Collections in this region South Sweden in 9 days
Southern Sweden, Götaland: a very varied area. In the south mainly flat, meadows, sea, views, beach, busy ports. More to the north, dense forests, hills, gravel roads, quiet towns (we would call them villages), lakes. And then Öland: a large, flat island with several surprises such as the two lighthouses, the Iron Age fortress on the southern tip, nice little harbours, castles and ruins, also of the Swedish royal couple. And wooden houses everywhere, nature, friendly people, space. The word "cute" sometimes crosses my mind. So knotty. The roads are mostly good, even the gravel roads are fine without any off-road experience or motorcycle. This route collection contains 9 routes of more than 2000 kilometers and takes you along the outer edges of Götaland: from Malmö along the east coast via Ystad, Karlshamm, Karlskrona and Kalmar to the island of Öland. From there the route heads inland to Vimmerby, back to the coast at Västervik, up to Linköping and Motala to the large Lake Vättern. Further down via Jonköping to Gothenburg on the west coast and then via a trip inland to enjoy the forests, lakes, gravel roads and nature via Varberg, Halmstad and Helsingborg back to Malmö.
The starting point is Malmö, at ""the bridge"" over the Kattengat between Denmark and Sweden. We drove there by taking the ferry from Puttgarden to Rødby and then crossing the bridge over the Danish islands of Lolland, Falster and Sjaelland via Copenhagen. But you can also take the ferry from Rostock to Trelleborg. Or you can drive all the way overland via Kolding and Odense in Denmark.
In addition to the sights below, there are special towns, nature reserves and castles/mansions in which route you can admire.
Route 1 goes along the coast of the southernmost tip of Sweden, the province of Skåne, through beautiful nature reserves and well-known towns such as Ystad to Karlshamm. Sights: a Viking village at Skanör, Skanör itself, Smygehuk (the southernmost tip of Sweden), Ystad (Wallander!), the stone formation at Käseberga, car museum at Simrishamn.
Route 2 goes through the province of Blekinge past towns like Ronneby and Kalmar to the island of Öland. Sights: kitesurf beach at Kristianopel, rock formation at Gettlinge, lighthouse Långe Jan.
Route 3 goes over Öland and then some more into the forests of the mainland towards Vimmerby. Sights: the ancient castle at Eketorp, Trollskogen (forest with strangely shaped trees and a beach with the wreck of a stranded boat), lighthouse Långe Erik, the special rock formations in the sea of Byrums raukar, Aboda lake and viewpoint.
Route 4 is a bit shorter because you then end at Vimmerby: the birthplace of Astrid Lindgren (from Pippi, among others). Sights: a moose park, an ancient oak, Vimmerby with Astrid Lindgren's amusement park and birth house annex museum.
Route 5 takes you back to the east coast at Västervik and then heads north and back inland to Linköping. Sights: a moose park (more beautiful than the previous day), a troll forest at Gamleby (ABBA city...), knight's castle Ekenäs, the Göta Canal with a lock complex.
Route 6 is also shorter and continues along the Göta Canal to Motala on Lake Vättern and then south to Gränna, where you can cross over to Visingsö Island. The route is shorter because you then have time to visit Visingsö. Sights: car and motorcycle museum and aquarium in Motala, Alvastra monastery ruins, Visingsö, observation tower, boat trip.
Route 7 takes you via Jönköping to Gothenburg. Sights: old wooden houses near Huskvarna (Jönköping) and of course Gothenburg.
Route 8 goes back into the country so you can enjoy the beautiful forests and lakes and gravel roads again. Then back to the coast with nice towns such as Varberg and Falkenberg. Sights: an old mill, a wooden bathhouse in the sea, beach, museum with remains of aircraft from the Second World War.
Route 9 takes you back to Malmö, although you can also cross over to Denmark earlier at Helsingborg. First you pass the beautiful city of Halmstad and the viewpoint at Mölle. Sights: a special bakery annex lunchroom, beach that can be driven on, lighthouse.
A collection with very varied routes, many sights with something for everyone, excellent roads and also pieces of gravel that can be ridden. Of course you can change the daily schedule by making routes longer, shortening or combining them. If you skip all the sights, you can also drive this in 7 days.
The starting point is Malmö, at ""the bridge"" over the Kattengat between Denmark and Sweden. We drove there by taking the ferry from Puttgarden to Rødby and then crossing the bridge over the Danish islands of Lolland, Falster and Sjaelland via Copenhagen. But you can also take the ferry from Rostock to Trelleborg. Or you can drive all the way overland via Kolding and Odense in Denmark.
In addition to the sights below, there are special towns, nature reserves and castles/mansions in which route you can admire.
Route 1 goes along the coast of the southernmost tip of Sweden, the province of Skåne, through beautiful nature reserves and well-known towns such as Ystad to Karlshamm. Sights: a Viking village at Skanör, Skanör itself, Smygehuk (the southernmost tip of Sweden), Ystad (Wallander!), the stone formation at Käseberga, car museum at Simrishamn.
Route 2 goes through the province of Blekinge past towns like Ronneby and Kalmar to the island of Öland. Sights: kitesurf beach at Kristianopel, rock formation at Gettlinge, lighthouse Långe Jan.
Route 3 goes over Öland and then some more into the forests of the mainland towards Vimmerby. Sights: the ancient castle at Eketorp, Trollskogen (forest with strangely shaped trees and a beach with the wreck of a stranded boat), lighthouse Långe Erik, the special rock formations in the sea of Byrums raukar, Aboda lake and viewpoint.
Route 4 is a bit shorter because you then end at Vimmerby: the birthplace of Astrid Lindgren (from Pippi, among others). Sights: a moose park, an ancient oak, Vimmerby with Astrid Lindgren's amusement park and birth house annex museum.
Route 5 takes you back to the east coast at Västervik and then heads north and back inland to Linköping. Sights: a moose park (more beautiful than the previous day), a troll forest at Gamleby (ABBA city...), knight's castle Ekenäs, the Göta Canal with a lock complex.
Route 6 is also shorter and continues along the Göta Canal to Motala on Lake Vättern and then south to Gränna, where you can cross over to Visingsö Island. The route is shorter because you then have time to visit Visingsö. Sights: car and motorcycle museum and aquarium in Motala, Alvastra monastery ruins, Visingsö, observation tower, boat trip.
Route 7 takes you via Jönköping to Gothenburg. Sights: old wooden houses near Huskvarna (Jönköping) and of course Gothenburg.
Route 8 goes back into the country so you can enjoy the beautiful forests and lakes and gravel roads again. Then back to the coast with nice towns such as Varberg and Falkenberg. Sights: an old mill, a wooden bathhouse in the sea, beach, museum with remains of aircraft from the Second World War.
Route 9 takes you back to Malmö, although you can also cross over to Denmark earlier at Helsingborg. First you pass the beautiful city of Halmstad and the viewpoint at Mölle. Sights: a special bakery annex lunchroom, beach that can be driven on, lighthouse.
A collection with very varied routes, many sights with something for everyone, excellent roads and also pieces of gravel that can be ridden. Of course you can change the daily schedule by making routes longer, shortening or combining them. If you skip all the sights, you can also drive this in 7 days.
View Route Collection
9 Routes
2197.73 km
40h 50m
