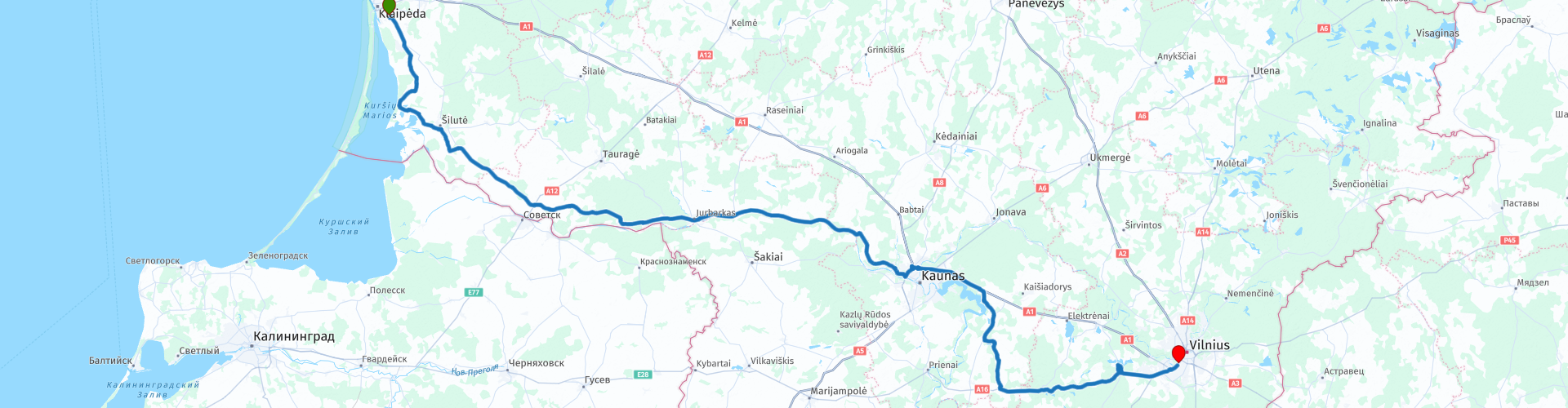
Klaipeda to Vilnius

This route was brought to you by:
RouteXpert Jannes van Dijken
Last edit: 28-01-2025
 Route Summary
Route Summary Lithuania is a lesser-known travel destination.
This route gives a good impression of what Lithuania has to offer.
I gave this route 4 stars because the historical points on and along the route give a good impression of what Lithuania is and was. The roads are well maintained.
Please note: This route includes a 4km stretch of gravel. This is easy to ride, but may not be the right choice during a rain shower.
 Share this route
Share this route 




Animation

Verdict


Duration
7h 52m

Mode of travel
Car or motorcycle

Distance
377.15 km

Countries


Vilnius
 RouteXpert Review
RouteXpert Review Lithuania has a diverse landscape of forests, lakes, rivers and coastlines. The country also has a number of national parks and nature reserves, such as the Aukštaitija National Park and the Aukštaimala Marsh.
Lithuania has a rich cultural heritage, with traditional folk music, dances and crafts still celebrated. The country also has a strong literary tradition and has produced many famous writers.
Since gaining independence from the Soviet Union in 1990, Lithuania has developed into a modern European state and is a member of the European Union and NATO.
The route begins in the port city of Klaipėda. Situated on the Baltic Sea coast, Klaipėda is the country's third largest city and its main port. Klaipėda has a rich history and is known by several names, including Memel, the German name of the city.
The city was first mentioned in 1252 and has had a complex history since then. It was part of the Teutonic Order, the Duchy of Prussia, the Kingdom of Prussia, and later the German Empire. After World War I, Klaipėda became part of Lithuania, but was annexed by Nazi Germany in 1939. After World War II, the city became part of the Lithuanian SSR and remained within Lithuania after independence in 1990.
Klaipėda is known for its historic architecture, including half-timbered houses and the neo-Baroque bridge portal of Queen Louise Bridge. The city also has several museums, such as the Mažosios Lietuvos istorijos muziejus and the Lithuanian Sea Museum.
Heading south, the route soon reaches the Aukštaimala Marsh. It is one of the largest wetlands in the country and has significant ecological value. In 1995, the Telmological Reserve Aukštaimala was established to protect and restore the unique ecosystem of the marsh. This area is of great importance due to its valuable habitats and the presence of rare and endangered species of flora and fauna.
The swamp is part of the territory of the Nemunas Delta Regional Park, an area known for its rich biodiversity and beautiful landscapes.
The Nemunas River, the natural border between Lithuania and the Russian Enclave of Kaliningrad, is the guiding principle of the route up to the city of Kaunas. The river, also known as the Neman, Niemen or Nioman, is a major river in Northeastern Europe. The river rises in Belarus, flows through Lithuania and forms part of the border with the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. With a length of approximately 937 kilometres, it is one of the longest rivers in the region.
The Nemunas River flows into the Curonian Lagoon, a lagoon connected to the Baltic Sea. The river is of great importance to the ecology and economy of the region, and its basin includes several valuable habitats and nature reserves, such as the Nemunas Delta Regional Park.
The river is also historically and culturally significant. In the town of Tilsit (now Sovetsk) the Treaty of Tilsit was signed in 1807 on a raft in the river.
Arriving in Kaunas, a stop is made at the Monument to the Victims of Nazism and the Ninth Fort. The monument is particularly impressive and takes your words away for a moment. The Ninth Fort is part of the Kaunas Fortress, which was built at the end of the 19th century. The fortress has a complex history and was used as a prison and a way station for prisoners transported to labor camps during the Soviet occupation. During the Nazi occupation of Lithuania, the fortress became a place of mass executions of Jews, captured Soviets and others.
Today, the Ninth Fort serves as a museum commemorating the victims of both Soviet and Nazi atrocities. The museum contains collections of historical artifacts related to these periods, as well as materials on the earlier history of Kaunas and the fortress itself.
After Kaunas the route continues towards the southeast. Here there is a gravel road of about 4 kilometers. Gravel roads are still common in Lithuania. They are usually well maintained and easy to drive on. During heavy rain showers it might be wise to avoid them.
The next photo stop is at Tarkai Island Castle. Trakai Island Castle is a beautiful medieval fortress located on an island in Lake Galvė, near the town of Trakai in Lithuania. The construction of the castle began in the 14th century by Grand Duke Kęstutis and was completed around 1409 by his son, Vytautas the Great. The castle played an important role in the history of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and served as a strategic military stronghold. The castle is known for its beautiful Gothic architecture and picturesque surroundings. It was badly damaged during several conflicts, but was carefully restored in the mid-20th century.
From Tarkai it is a short drive to Vilnius, the capital of Lithuania. It is a city with a rich history and vibrant culture. Situated at the confluence of the Neris and Vilnia rivers, Vilnius is known for its beautiful old town, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city has a unique mix of Gothic, Renaissance, Baroque and neoclassical architecture. Worth visiting in Vilnius include Gediminas Tower, which is a remnant of the Upper Vilnius Castle and offers a beautiful view of the city. Vilnius Cathedral: An impressive neoclassical cathedral located on Cathedral Square. And finally, the Gate of Dawn: One of the most important religious, historical and cultural monuments in the city.

Monument to commemorate the victims of Nazism

Trakai Island Castle
 Usage
Usage Want to download this route?
You can download the route for free without MyRoute-app account. To do so, open the route and click 'save as'. Want to edit this route?
No problem, start by opening the route. Follow the tutorial and create your personal MyRoute-app account. After registration, your trial starts automatically.  Disclaimer
Disclaimer
Use of this GPS route is at your own expense and risk. The route has been carefully composed and checked by a MyRoute-app accredited RouteXpert for use on TomTom, Garmin and MyRoute-app Navigation.
Changes may nevertheless have occurred due to changed circumstances, road diversions or seasonal closures. We therefore recommend checking each route before use.
Preferably use the route track in your navigation system. More information about the use of MyRoute-app can be found on the website under 'Community' or 'Academy'.
Changes may nevertheless have occurred due to changed circumstances, road diversions or seasonal closures. We therefore recommend checking each route before use.
Preferably use the route track in your navigation system. More information about the use of MyRoute-app can be found on the website under 'Community' or 'Academy'.

Klaipda
About this region
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, and the Russian semi-exclave of Kaliningrad Oblast to the southwest, with a maritime border with Sweden to the west. Lithuania covers an area of 65,300 km2 (25,200 sq mi), with a population of 2.89 million. Its capital and largest city is Vilnius; other major cities include Kaunas, Klaipėda, Šiauliai and Panevėžys. Lithuanians belong to the linguistic group of the Balts and speak Lithuanian.
For millennia, the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, Lithuanian lands were united for the first time by Mindaugas, who formed the Kingdom of Lithuania on 6 July 1253. Subsequent expansion and consolidation resulted in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, which by the 14th century was the largest country in Europe. In 1386, the Grand Duchy entered into a de facto personal union with the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. The two realms were united into the bi-confederal Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1569, forming one of the largest and most prosperous states in Europe. The Commonwealth lasted more than two centuries, until neighbouring countries gradually dismantled it between 1772 and 1795, with the Russian Empire annexing most of Lithuania's territory.
Towards the end of World War I, Lithuania declared Independence in 1918, founding the modern Republic of Lithuania. In World War II, Lithuania was occupied by the Soviet Union, then by Nazi Germany, before being reoccupied by the Soviets in 1944. Lithuanian armed resistance to the Soviet occupation lasted until the early 1950s. On 11 March 1990, a year before the formal dissolution of the Soviet Union, Lithuania became the first Soviet republic to break away when it proclaimed the restoration of its independence.
Lithuania is a developed country with a high income and an advanced economy. Lithuania is a member of the European Union, the Council of Europe, the eurozone, the Nordic Investment Bank, the Schengen Agreement, NATO, and OECD. It also participates in the Nordic-Baltic Eight (NB8) regional co-operation format.
Read more on Wikipedia
For millennia, the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, Lithuanian lands were united for the first time by Mindaugas, who formed the Kingdom of Lithuania on 6 July 1253. Subsequent expansion and consolidation resulted in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, which by the 14th century was the largest country in Europe. In 1386, the Grand Duchy entered into a de facto personal union with the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. The two realms were united into the bi-confederal Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1569, forming one of the largest and most prosperous states in Europe. The Commonwealth lasted more than two centuries, until neighbouring countries gradually dismantled it between 1772 and 1795, with the Russian Empire annexing most of Lithuania's territory.
Towards the end of World War I, Lithuania declared Independence in 1918, founding the modern Republic of Lithuania. In World War II, Lithuania was occupied by the Soviet Union, then by Nazi Germany, before being reoccupied by the Soviets in 1944. Lithuanian armed resistance to the Soviet occupation lasted until the early 1950s. On 11 March 1990, a year before the formal dissolution of the Soviet Union, Lithuania became the first Soviet republic to break away when it proclaimed the restoration of its independence.
Lithuania is a developed country with a high income and an advanced economy. Lithuania is a member of the European Union, the Council of Europe, the eurozone, the Nordic Investment Bank, the Schengen Agreement, NATO, and OECD. It also participates in the Nordic-Baltic Eight (NB8) regional co-operation format.
View region
 Statistics
Statistics  1
1Amount of RX reviews (Klaipda)
 50
50Amount of visitors (Klaipda)
 0
0Amount of downloads (Klaipda)

 Links
Links