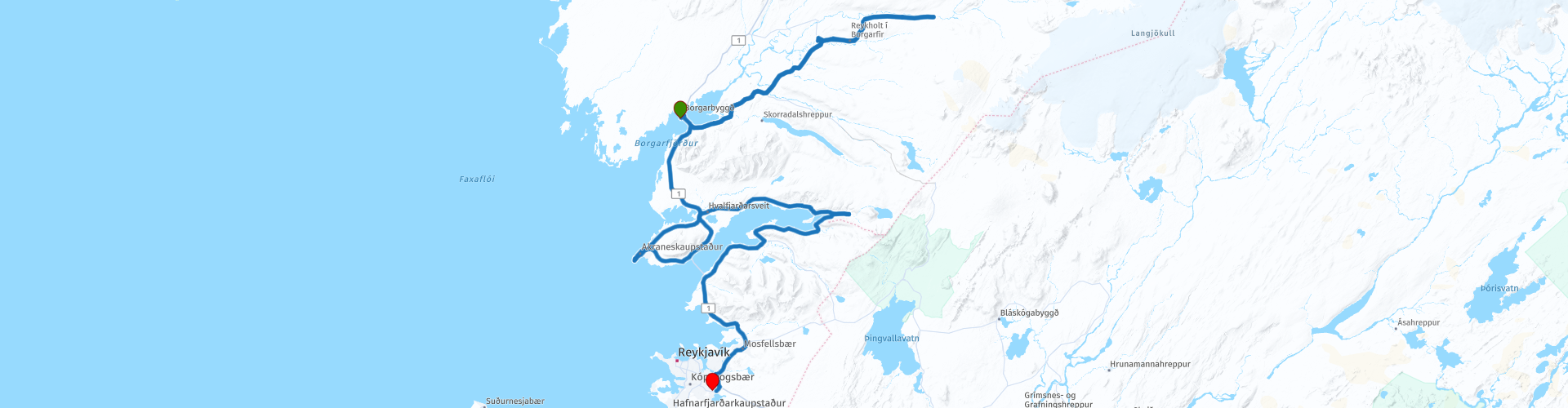
Day 12 of 12 Day Roadtrip Iceland Borgarnes Reykjavik

This route was brought to you by:
RouteXpert René Plücken (MRA Master)
Last edit: 12-02-2021
 Route Summary
Route Summary Driving in Iceland is a great experience whether you travel by car or as described in this review by motorcycle.
These routes are based on information about Iceland that you can find on the Internet, especially from the Guide to Iceland, where you can find a wealth of information to prepare you well for your trip. The material on this site has been compiled with great care, the link can be found in the review of the first route in this series.
You drive through landscapes that are varied and beautiful, you see glacier tongues, volcanic mountains, geothermal areas with active geysers, lava fields, craters, forests, waterfalls and incredibly rugged stretches of coast.
The routes in the north are part of the 'Arctic Coast Way'.
The main roads are of good quality but you also drive a lot on gravel roads, so not suitable for road motorcycles. Some of these roads are sometimes closed due to the weather. It is therefore important that you check the weather forecasts and the situation of the roads every day before you leave, this information can be found on the website of "Icelandic Meteorological Office" and for the roads on the website of "The Icelandic Road and Coastal Administration" " The links are in the review.
Due to the Icelandic climate, this trip can only be made in the summer.
 Share this route
Share this route 




Animation

Verdict


Duration
4h 26m

Mode of travel
Car or motorcycle

Distance
269.69 km

Countries


Hafnarfjall Mountains (RP10)
 RouteXpert Review
RouteXpert Review Deildartunguhver has the highest flow of hot springs in Europe. The hot water pump pumps 180 liters of water at 100 ° C (212 ° F) per second, which is partly used to provide geothermal heat for houses in West Iceland.
Visit Deildartunguhver to witness this true natural power or better yet, take a bath in the pure water from the hot spring at Krauma Geothermal Nature Baths.
The next stop is planned at the historic village of Reykholt (RP6). Reykholt is one of the most remarkable historical sights of Iceland. It is best known by the home of Iceland's best-known author Snorri Sturluson from 1206-1241. An old geothermal heated swimming pool, Snorralaug, is named after him. It is one of the few things that have been preserved throughout the medieval period of Iceland. Snorrastofa is a cultural center and institute for research in medieval studies and offers historical exhibitions, tours and lectures. Music recitals are held in the church of Reykholt.
After enjoying scenic Reykholt, head further east on Route 518 to reach the Barnafoss and Hraunfossar (RP7) waterfalls.
Barnafoss is a rapid waterfall that makes its way through a narrow gorge; the name means 'the waterfall of the children' because of the macabre history of two boys who fall from a bridge that has since been destroyed to their death.
Hraunfossar is relatively serene; it is not high, but very wide and the water seeps through the lava rock in many quiet streams. Despite how different they are, these waterfalls are within walking distance of each other. There is a café-restaurant nearby if there is a need for refreshments.
We drive back via Route 518, then south along Route 50 to the Trolls waterfalls in Fossatún (RP9). This is a great area for children, but also for adults, as there are many small elf houses, troll statues and information posts about Iceland's folklore within a short walk. At the hotel restaurant there is possibility for lunch.
Continue south on route 50 and again take route 1 at Borgarnes around the imposing Hafnarfjall mountains, at RP10 there is a small parking lot with information signs about this mountain. This is also a nice place to take a photo.
The next stop to take a picture of a beautiful view of the sea is at the Old Akranes Lighthouse (RP12), actually there are two lighthouses. If you drive to the port, you will already see two lighthouses. The larger one currently in use is open to the public. The smaller lighthouse is one of the oldest concrete lighthouses in Iceland and was built in 1918. It served the fishing village until it was deactivated in 1947 in favor of the larger.
We continue along the Hvalfjörður fjord (RP15), a green, mountainous fjord.
At RP16 we turn left to park at the end at a footpath to the second highest waterfall in Iceland; de Glymur (16) this is the last place you visit on this incredible 12-day road trip.
The Glymur with its 196 meters is the highest waterfall in Iceland. It lies in the Botnsá River that flows from the 160-meter-deep Hvalvatn to the Hvalfjörður in southwest Iceland. The waterfall is not as well known, possibly because the lower part falls into a narrow deep gap and is therefore hidden from view.
After marveling at the height and splendor of Glymur, you can follow Route 47 along the other side of the fjord until you reach Route 1 that leads back to Reykjavík.
This last route of the 12 day Roadtrip through Iceland was a nice ending that is worth 4 **** Stars.

RP5 Deildartunguhver Thermal Springs

RP15 Hvalfjörður fjord
 Links
Links  Usage
Usage Want to download this route?
You can download the route for free without MyRoute-app account. To do so, open the route and click 'save as'. Want to edit this route?
No problem, start by opening the route. Follow the tutorial and create your personal MyRoute-app account. After registration, your trial starts automatically.  Disclaimer
Disclaimer
Use of this GPS route is at your own expense and risk. The route has been carefully composed and checked by a MyRoute-app accredited RouteXpert for use on TomTom, Garmin and MyRoute-app Navigation.
Changes may nevertheless have occurred due to changed circumstances, road diversions or seasonal closures. We therefore recommend checking each route before use.
Preferably use the route track in your navigation system. More information about the use of MyRoute-app can be found on the website under 'Community' or 'Academy'.
Changes may nevertheless have occurred due to changed circumstances, road diversions or seasonal closures. We therefore recommend checking each route before use.
Preferably use the route track in your navigation system. More information about the use of MyRoute-app can be found on the website under 'Community' or 'Academy'.

Iceland
About this region
Iceland (Icelandic: Ísland; [ˈistlant] (listen)) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and the most sparsely populated country in Europe. The capital and largest city is Reykjavík. Reykjavík and the surrounding areas in the southwest of the country are home to over two-thirds of the population. Iceland is the only part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that rises above sea-level, and its central volcanic plateau is erupting almost constantly. The interior consists of a plateau characterised by sand and lava fields, mountains, and glaciers, and many glacial rivers flow to the sea through the lowlands. Iceland is warmed by the Gulf Stream and has a temperate climate, despite a high latitude just outside the Arctic Circle. Its high latitude and marine influence keep summers chilly, and most of its islands have a polar climate.
According to the ancient manuscript Landnámabók, the settlement of Iceland began in 874 AD when the Norwegian chieftain Ingólfr Arnarson became the first permanent settler on the island. In the following centuries, Norwegians, and to a lesser extent other Scandinavians, emigrated to Iceland, bringing with them thralls (i.e., slaves or serfs) of Gaelic origin.
The island was governed as an independent commonwealth under the Althing, one of the world's oldest functioning legislative assemblies. Following a period of civil strife, Iceland acceded to Norwegian rule in the 13th century. The establishment of the Kalmar Union in 1397 united the kingdoms of Norway, Denmark, and Sweden. Iceland thus followed Norway's integration into that union, coming under Danish rule after Sweden's secession from the union in 1523. Although the Danish kingdom introduced Lutheranism forcefully in 1550, Iceland remained a distant semi-colonial territory in which Danish institutions and infrastructures were conspicuous by their absence.In the wake of the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Wars, Iceland's struggle for independence took form and culminated in independence in 1918 and the founding of a republic in 1944. Although its parliament (Althing) was suspended from 1799 to 1845, the island republic has been credited with sustaining the world's oldest and longest-running parliament.
Until the 20th century, Iceland relied largely on subsistence fishing and agriculture. Industrialization of the fisheries and Marshall Plan aid following World War II brought prosperity, and Iceland became one of the wealthiest and most developed nations in the world. It became a part of the European Economic Area in 1994; this further diversified the economy into sectors such as finance, biotechnology, and manufacturing.
Iceland has a market economy with relatively low taxes, compared to other OECD countries, as well as the highest trade union membership in the world. It maintains a Nordic social welfare system that provides universal health care and tertiary education for its citizens. Iceland ranks high in economic, democratic, and social stability, as well as equality, ranking third in the world by median wealth per adult. In 2020, it was ranked as the fourth-most developed country in the world by the United Nations' Human Development Index, and it ranks first on the Global Peace Index. Iceland runs almost completely on renewable energy.
Icelandic culture is founded upon the nation's Scandinavian heritage. Most Icelanders are descendants of Norse and Gaelic settlers. Icelandic, a North Germanic language, is descended from Old West Norse and is closely related to Faroese. The country's cultural heritage includes traditional Icelandic cuisine, Icelandic literature, and medieval sagas. Iceland has the smallest population of any NATO member and is the only one with no standing army, with a lightly armed coast guard.
Read more on Wikipedia
According to the ancient manuscript Landnámabók, the settlement of Iceland began in 874 AD when the Norwegian chieftain Ingólfr Arnarson became the first permanent settler on the island. In the following centuries, Norwegians, and to a lesser extent other Scandinavians, emigrated to Iceland, bringing with them thralls (i.e., slaves or serfs) of Gaelic origin.
The island was governed as an independent commonwealth under the Althing, one of the world's oldest functioning legislative assemblies. Following a period of civil strife, Iceland acceded to Norwegian rule in the 13th century. The establishment of the Kalmar Union in 1397 united the kingdoms of Norway, Denmark, and Sweden. Iceland thus followed Norway's integration into that union, coming under Danish rule after Sweden's secession from the union in 1523. Although the Danish kingdom introduced Lutheranism forcefully in 1550, Iceland remained a distant semi-colonial territory in which Danish institutions and infrastructures were conspicuous by their absence.In the wake of the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Wars, Iceland's struggle for independence took form and culminated in independence in 1918 and the founding of a republic in 1944. Although its parliament (Althing) was suspended from 1799 to 1845, the island republic has been credited with sustaining the world's oldest and longest-running parliament.
Until the 20th century, Iceland relied largely on subsistence fishing and agriculture. Industrialization of the fisheries and Marshall Plan aid following World War II brought prosperity, and Iceland became one of the wealthiest and most developed nations in the world. It became a part of the European Economic Area in 1994; this further diversified the economy into sectors such as finance, biotechnology, and manufacturing.
Iceland has a market economy with relatively low taxes, compared to other OECD countries, as well as the highest trade union membership in the world. It maintains a Nordic social welfare system that provides universal health care and tertiary education for its citizens. Iceland ranks high in economic, democratic, and social stability, as well as equality, ranking third in the world by median wealth per adult. In 2020, it was ranked as the fourth-most developed country in the world by the United Nations' Human Development Index, and it ranks first on the Global Peace Index. Iceland runs almost completely on renewable energy.
Icelandic culture is founded upon the nation's Scandinavian heritage. Most Icelanders are descendants of Norse and Gaelic settlers. Icelandic, a North Germanic language, is descended from Old West Norse and is closely related to Faroese. The country's cultural heritage includes traditional Icelandic cuisine, Icelandic literature, and medieval sagas. Iceland has the smallest population of any NATO member and is the only one with no standing army, with a lightly armed coast guard.
View region
 Statistics
Statistics  18
18Amount of RX reviews (Iceland)
 13884
13884Amount of visitors (Iceland)
 576
576Amount of downloads (Iceland)
 Route Collections in this region
Route Collections in this region On an adventure in Iceland
12 Day Iceland Road Trip
Driving in Iceland is a great experience whether you travel by car or as described in this review by motorcycle.
This route collection is based on information about Iceland that you can find on the Internet, especially from the Guide to Iceland, where you can find a wealth of information to prepare you well for your trip.
You drive through landscapes that are varied and beautiful, you see glacier tongues, volcanic mountains, geothermal areas with active geysers, lava fields, craters, forests, waterfalls and incredibly rugged stretches of coast. You will also see many animals such as seals, killer whales, humpback whales, puffins, gulls, olives and petrels
The main roads are of good quality but you also drive a lot on gravel roads, so not suitable for road motorcycles. Some of these roads are sometimes closed due to the weather.
It is therefore important that you check the weather forecasts and the situation of the roads every day before you leave, this information can be found on the website of "Icelandic Meteorological Office" and for the roads on the website of "The Icelandic Road and Coastal Administration" "
Due to the Icelandic climate this trip can only be made in the summer and is suitable for car and motorcycle. Renting cars (also 4x4) and motorbikes is possible in Reykjavik.
If you want your own car or motorcycle, you can make a ferry crossing from the Netherlands or Denmark via the Faroe Islands. Then take another week off for the crossings, or longer because you can also make beautiful rides on Faroe Islands.
This route collection consists of the following routes
Day 1 from Reykjavik to Vik (350km)
Day 2 from Vik to Kirkjubaejarklaustur (215km)
Day 3 from Kirkjubaejarklaustur to Hoefn (225km)
Day 4 from Hoefn to Seydisfjoerdur (295km)
Day 5 from Seydisfjoerdur to Husavik (300km)
Day 6 from Husavik to Siglufjordur (260km)
Day 7 from Siglufjordur to Blonduos (220km)
Day 8 from Blonduos to Reykholar (325km)
Day 9 from Reykholar to Patreksfjordur (455km)
Day 10 from Patreksfjordur to Grundarfjordur (280km)
Day 11 from Grundarfjordur to Borgarnes (210km)
Day 12 from Borgarnes to Reykjavik (270km)
Driving in Iceland is a great experience whether you travel by car or as described in this review by motorcycle.
This route collection is based on information about Iceland that you can find on the Internet, especially from the Guide to Iceland, where you can find a wealth of information to prepare you well for your trip.
You drive through landscapes that are varied and beautiful, you see glacier tongues, volcanic mountains, geothermal areas with active geysers, lava fields, craters, forests, waterfalls and incredibly rugged stretches of coast. You will also see many animals such as seals, killer whales, humpback whales, puffins, gulls, olives and petrels
The main roads are of good quality but you also drive a lot on gravel roads, so not suitable for road motorcycles. Some of these roads are sometimes closed due to the weather.
It is therefore important that you check the weather forecasts and the situation of the roads every day before you leave, this information can be found on the website of "Icelandic Meteorological Office" and for the roads on the website of "The Icelandic Road and Coastal Administration" "
Due to the Icelandic climate this trip can only be made in the summer and is suitable for car and motorcycle. Renting cars (also 4x4) and motorbikes is possible in Reykjavik.
If you want your own car or motorcycle, you can make a ferry crossing from the Netherlands or Denmark via the Faroe Islands. Then take another week off for the crossings, or longer because you can also make beautiful rides on Faroe Islands.
This route collection consists of the following routes
Day 1 from Reykjavik to Vik (350km)
Day 2 from Vik to Kirkjubaejarklaustur (215km)
Day 3 from Kirkjubaejarklaustur to Hoefn (225km)
Day 4 from Hoefn to Seydisfjoerdur (295km)
Day 5 from Seydisfjoerdur to Husavik (300km)
Day 6 from Husavik to Siglufjordur (260km)
Day 7 from Siglufjordur to Blonduos (220km)
Day 8 from Blonduos to Reykholar (325km)
Day 9 from Reykholar to Patreksfjordur (455km)
Day 10 from Patreksfjordur to Grundarfjordur (280km)
Day 11 from Grundarfjordur to Borgarnes (210km)
Day 12 from Borgarnes to Reykjavik (270km)
View Route Collection
12 Routes
3406.93 km
63h 38m
Adventure Tour along the Arctic Coast Way in Iceland
Iceland is a pearl on the earth with many natural beauties. In 2019, the Arctic Coast Way was opened to allow travelers to enjoy untouched nature. The Arctic Coast Way is a great opportunity to see wildlife, dive geothermal pools and take part in adventure activities such as hiking, boating and horseback riding, surrounded by sea and mountain views.
The Arctic Coast Way starts in Hvammstangi in the north-west and ends in Bakkafjörður in the north-east. This approximately 900 kilometer long “Off the Beaten track” route passes through rugged North Iceland and follows the beautiful Fjord coast.
Driving the Arctic Coast Way is different from what you might be used to. It is a true off the beaten track route that takes you through beautiful remote landscapes. This means leaving civilization behind in the spirit of adventure and exploration.
We drive large parts on unpaved roads (about 1/3 part), sometimes with large holes, so this route is only suitable for Adventure or Off Road motorcycles or cars with 4x4 drive. Drive slowly to enjoy the magical surroundings but because of the sheep and birds that can walk on the road.
The route runs close to the Arctic Circle and many stops are planned along the way to visit Iceland's many highlights. A number of examples are the many waterfalls, glaciers, fishing villages and fjords. In some cases you have to take a walk (hike), these can influence the planning of the rides, so keep that in mind. Due to the slower speed on the unpaved roads and the sights along the way, the routes have been kept short.
Enjoy the freedom along the way, but respect nature and keep in mind that wild camping is prohibited, you are only allowed to camp on campsites or with the permission of the owner on his private property. All villages along the route have camping options. All campsites have rubbish bins and sanitary facilities. Do not drive off-road, but stay on the designated roads. Off-road driving is prohibited, with heavy fines.
The routes are;
Day 1 from Hvammstangi to Blönduós
Day 2 from Blönduós to Grettislaug
Day 3 from Grettislaug to Siglufjörður
Day 4 from Siglufjörður to Húsavik
Day 5 from Húsavik to Raufarhöfn
Day 6 from Raufarhöfn to Bakkafjörður
The Arctic Coast Way starts in Hvammstangi in the north-west and ends in Bakkafjörður in the north-east. This approximately 900 kilometer long “Off the Beaten track” route passes through rugged North Iceland and follows the beautiful Fjord coast.
Driving the Arctic Coast Way is different from what you might be used to. It is a true off the beaten track route that takes you through beautiful remote landscapes. This means leaving civilization behind in the spirit of adventure and exploration.
We drive large parts on unpaved roads (about 1/3 part), sometimes with large holes, so this route is only suitable for Adventure or Off Road motorcycles or cars with 4x4 drive. Drive slowly to enjoy the magical surroundings but because of the sheep and birds that can walk on the road.
The route runs close to the Arctic Circle and many stops are planned along the way to visit Iceland's many highlights. A number of examples are the many waterfalls, glaciers, fishing villages and fjords. In some cases you have to take a walk (hike), these can influence the planning of the rides, so keep that in mind. Due to the slower speed on the unpaved roads and the sights along the way, the routes have been kept short.
Enjoy the freedom along the way, but respect nature and keep in mind that wild camping is prohibited, you are only allowed to camp on campsites or with the permission of the owner on his private property. All villages along the route have camping options. All campsites have rubbish bins and sanitary facilities. Do not drive off-road, but stay on the designated roads. Off-road driving is prohibited, with heavy fines.
The routes are;
Day 1 from Hvammstangi to Blönduós
Day 2 from Blönduós to Grettislaug
Day 3 from Grettislaug to Siglufjörður
Day 4 from Siglufjörður to Húsavik
Day 5 from Húsavik to Raufarhöfn
Day 6 from Raufarhöfn to Bakkafjörður
View Route Collection
6 Routes
999.35 km
63h 8m
